- Introduction: Safeguarding Electrical Systems with Voltage Fuses
- What Is a Voltage Fuse?
- Key Functions:
- Applications of Voltage Fuses
- Common Application Areas:
- Market Trends and Technological Developments
- Industry Shifts:
- Technical Specifications of Voltage Fuses
- Comparison with Other Protective Devices
- How to Select the Right Voltage Fuse
- 1. Rated Voltage & Current
- 2. Breaking Capacity
- 3. Time-Current Characteristics
- 4. Environment & Mounting
- 5. Compliance Standards
- Industry References and Standards
- FAQs About Voltage Fuses
Introduction: Safeguarding Electrical Systems with Voltage Fuses
In the complex world of electrical engineering, safety is paramount. Among the many protective devices used across power distribution systems, the voltage fuse stands as one of the most critical components for preventing equipment damage and electrical fires. But what exactly is a voltage fuse, and why is it indispensable in both residential and industrial applications?
This article explores the function, application, market relevance, and technical aspects of voltage fuses while offering practical guidance for selecting the right type.
What Is a Voltage Fuse?
A voltage fuse is a type of overcurrent protection device designed to interrupt the flow of electricity when the current exceeds a certain threshold. It works by melting a fusible element inside its casing, effectively breaking the circuit and stopping the flow of current to downstream devices.
Key Functions:
- Overcurrent protection: Prevents overheating or fire due to excess current.
- Short-circuit protection: Interrupts dangerous fault currents immediately.
- System isolation: Assists in isolating faulty components without damaging healthy ones.
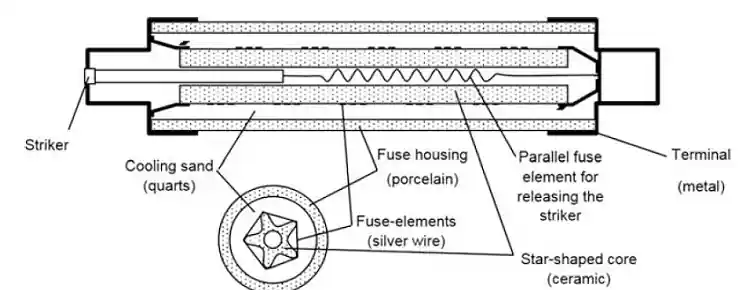
Applications of Voltage Fuses
Voltage fuses are used in a variety of sectors where electrical protection is necessary. Their design varies according to voltage level, type of circuit, and specific protection requirements.
Common Application Areas:
- Medium to High-Voltage Switchgear Systems
- Transformers and Substations
- Renewable Energy Systems (Solar PV, Wind)
- HVAC and Industrial Control Panels
- Power Distribution Units (PDUs)
In high-voltage environments such as substations (e.g., 11kV or 33kV systems), voltage fuses are used in conjunction with circuit breakers and disconnect switches for comprehensive protection.

Market Trends and Technological Developments
The voltage fuse market has experienced consistent growth due to increasing energy demand, infrastructure development, and renewable energy integration. According to a 2024 report by Markets and Markets, the global fuse market is expected to surpass USD 5.5 billion by 2028.
Additionally, international standards such as IEC 60282 for high-voltage fuses and IEEE Std C37.41 define test methods and performance guidelines to ensure safety and compatibility.
Industry Shifts:
- Smarter Fuses: Integration of monitoring chips for predictive failure alerts.
- Eco-Friendly Materials: Lead-free and halogen-free designs.
- Miniaturization: Compact form factors for space-saving panels.
Reference: IEEE Explore, ABB Technical Papers, Schneider Electric Whitepapers
Technical Specifications of Voltage Fuses
Below is a general specification chart for high-voltage fuses used in switchgear and transformer protection:
| Parameter | Typical Value |
|---|---|
| Rated Voltage | 12kV – 36kV |
| Rated Current | 10A – 200A |
| Breaking Capacity | Up to 50kA |
| Fuse Link Material | Silver, Copper |
| Operating Time (Fast Blow) | < 1 millisecond |
| Standard Compliance | IEC 60282-1, ANSI C37.41 |
| Fuse Type | Expulsion Fuse, Cartridge Fuse |
| Installation Type | Indoor/Outdoor, Vertical/Horizontal |
Comparison with Other Protective Devices
Voltage fuses are often compared with circuit breakers and relays in electrical systems. Here’s how they differ:
| Criteria | Voltage Fuse | Circuit Breaker |
|---|---|---|
| Operation | Melts on overcurrent | Switches off via mechanical mechanism |
| Reset Capability | Non-resettable (one-time use) | Resettable |
| Reaction Time | Very fast (sub-millisecond) | Slightly slower |
| Maintenance | Minimal | Requires periodic servicing |
| Cost | Generally lower | Higher initial cost |
Voltage fuses are highly reliable in fault isolation and are particularly useful in areas where faults must be cleared very quickly.
How to Select the Right Voltage Fuse
Choosing the correct fuse is essential for ensuring both protection and continuity of service. The following criteria should be considered:
1. Rated Voltage & Current
Ensure the fuse’s ratings match or exceed the system requirements. For instance, in a 12kV system, choose a fuse rated at or above 12kV with suitable ampere rating.
2. Breaking Capacity
Check the maximum fault current your system can experience. Select a fuse that can safely interrupt this current without rupturing.
3. Time-Current Characteristics
Fast-blow fuses are ideal for sensitive equipment, while slow-blow fuses accommodate short inrush currents without tripping.
4. Environment & Mounting
Consider indoor vs. outdoor installation, temperature range, and humidity conditions.
5. Compliance Standards
Always choose products that conform to international standards like IEC, ANSI, or IS to ensure reliability and safety.
Industry References and Standards
To validate selection and ensure safety, refer to well-established global resources:
- IEEE Std C37.41 – Standard for High-Voltage Fuses
- IEC 60282-1 – Fuses for high-voltage applications
- Wikipedia – Voltage Fuse Overview
- ABB Switchgear Protection Guide
- Schneider Electric Tech Library
- IEEMA – Indian Electrical & Electronics Manufacturers’ Association insights
These references provide reliable data for engineers and buyers alike, enhancing both credibility and informed decision-making.
FAQs About Voltage Fuses
When the current exceeds the fuse’s rated capacity, the internal fusible link melts, breaking the circuit. This helps prevent further damage or fire. The fuse must be replaced before the circuit can resume operation.
No. Voltage fuses are single-use protection devices. Once blown, they must be replaced with an identical-rated fuse to restore circuit protection.
Yes. Modern fuse designs incorporate diagnostics and environmental resilience, making them compatible with evolving smart grid technologies, including renewable energy sources and automated substations.
Voltage fuses may appear simple, but their role in maintaining the safety and stability of electrical systems is profound. Whether protecting a residential Transformer guide or a 33kV substation switchgear, the right fuse ensures rapid response to faults and minimizes risk.
Understanding fuse specifications, application areas, and proper selection criteria empowers engineers and procurement specialists to design safer and more efficient systems.

